Electrical cables contain one or more insulated conductors. These are often a conductive layer, a shielded wire, or a Shielded cable surround it. These wires help in securing the safety of electrical wires that run through your house or property. In general, shielded cables can also prevent various electrical disturbances, such as electrical disturbances and noise from various heavy machinery in the workplace.
Shielded cables can have a major impact on your business. Do you want to know more specifically? Please continue to read it.
Get Your Free Sample!
Explore our custom services now. Email us at [email protected] for more details.
Chapter 1: A Shielded Cable and its Features
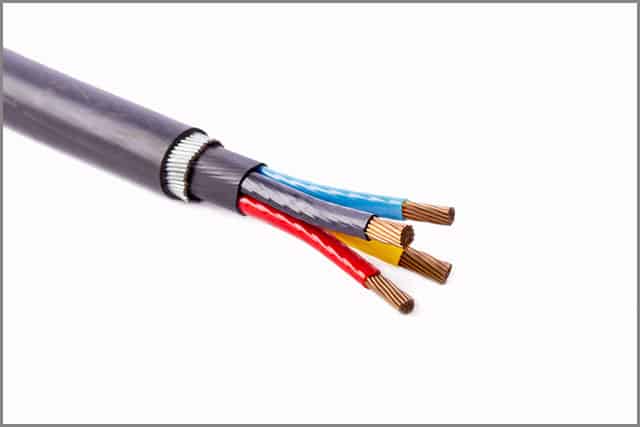

A shield is generally an electrically conductive substance. It surrounds a wire or cable, which prohibits any signal getaway. The shielding of the cable, in turn, is simply enclosing the inner signals or power-carrying conductors. Shielded cables interact differently with electromagnetic interference (EMI). They can be both a source of EMI as well as a receiver. As a source, cables can radiate signals to other cables and even act as an antenna that radiates noise.
The cable can also act as a receiver. It receives these signals from other cables and generates EMI through your office floor. When switching any big loads of power, such as huge transformers, powerful heaters, it is enough to trigger a noticeable EMI amount.
These disturbances or feedbacks can also take place when placing a signal cable next to a power cable. Most industries and their factory floors are always making a lot of noise. It is because of unshielded cables that cause this level of interference and is very hazardous for industry workers and laborers. Therefore, installing shielded cables will improve your factory’s working conditions. It will also ensure every worker’s safety.

Applications of Shielded Cables
There are various ways you can apply for shielded cables. The need for shielding your electrical cables comes from the amount of power your factory generates every. It also depends on the type of factory you have. Different factories and manufacturing units can emit various levels of electronic interference. Some of them are:
• High level of electrical noise:
These noises normally come from:
- heavy motors
- electrolytic processes
- control lines a
- power lines
The proximity of power lines generates these noises and disturbances. Typical locations where you can find these noises – Steel mills and Foundries.
• Medium level of electrical noise:
Average manufacturing plants create these electrical noises.
These plants need to operate heavy control relays and wiring near powerful or medium-sized motors.
• Low level of electrical interference:
You may face these disturbances where the main power source is far from the wiring. Also, when control and power relays are nearby. The typical locations where you can find this kind of interference are:
- Big storage areas
- Offices
- Laboratories
- Small Scale Operating Plants
Thus, stop any EMI generation on your office floor by installing shielded cables. Shielded cables installed on normal electrical wires can make your workplace better and safe.

Chapter 2: Importance and emergence of Shielded Cables
We are advancing day by day in various aspects of life. Technological advancement has surely benefited us. It has pushed us more to learn, discover, and recreate new possibilities. Cables are an essential part of today’s fast pacing communication. For example, think what would happen if Google collapsed in a single state or city for just one hour or a day? There would be chaos around.
People will lose money, time, and many other assets if a strong communication system such as Google fails to deliver its services. Today’s modern world does not view the cable as just four wires bound by a casing connecting electronic devices. Cables have become the most important medium of communication. Most of the world’s communication system entirely depends on shielded and unshielded cables.
If you know for what purpose you will use a cable, you also need to know about the required power output. It is also important to ensure your device’s protection from the power output’s frequency. Electromagnetic disturbances can also harm your device. It is where you need to decide whether you want to shield your cable or leave it unshielded.
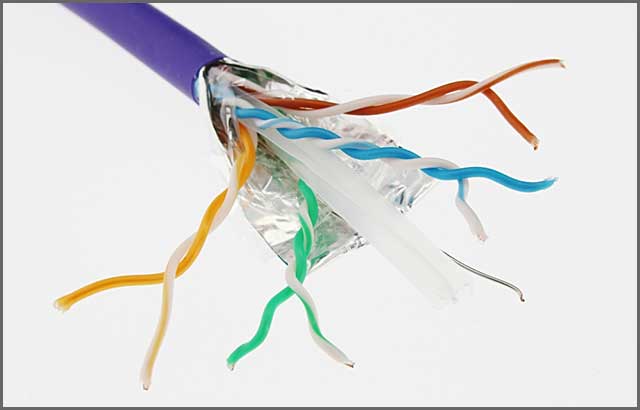

Here is why using a shielded cable is so important.
• Preventing Electromagnetic Interferences (EMI)
External sources of electrical energy generate radio frequency interference or electromagnetic interference. These sources are often electrical circuit noises, electromagnetic radiation coming from power lines. We are all surrounded by EMI/RFI. It’s just like when you hear static noises from a phone. The same goes for networking in terms of communication.
To put it even more simply, if the EMI noise is strong enough, you may find that you are losing a lot of data. It happens when your machines are not being able to hear each other properly. It happens because of the EMI/RFI. Neglecting these issues may be harmful and dangerous for your workers and employees and can cause huge losses to your business.
To choose the correct shielded cable, you need to select from the available cables for different purposes.
Learn about cable shielding and armor here.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aHqwRVKFtqE
Get Your Free Sample!
Explore our custom services now. Email us at [email protected] for more details.
Chapter 3: The Popular Types of Shielding
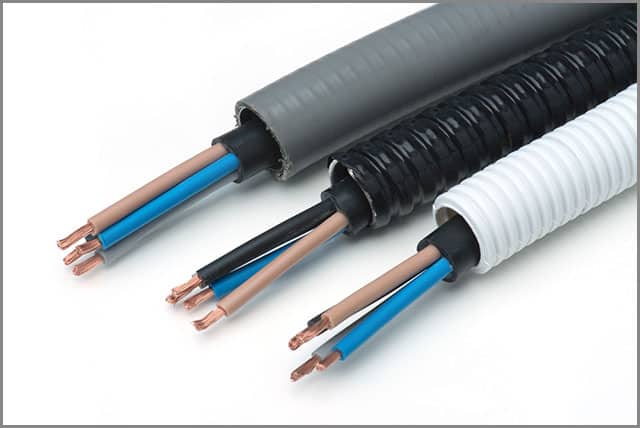

Not allowing any external interference, be it electrical or magnetic is the primary function of a shielded cable. As there are many kinds of businesses and factories with diverse usage of power input and output, there are many types of shielding. Making a shielded cable can involve using corrugated metals, braids, and many other materials. It also affects the cable’s functions and features. These features depend entirely on the purpose of your requirement.
Here are some popular types of shielding you can choose from:
Braided Shielding
This type or form of shielding is the oldest kind of shielding. Manufacturers still practice this format present times. The process of making small gauge wires in a woven pattern defines braided shielding. Braids are usually made up of copper, aluminium, steel, and tinned copper, and weave it on the conductor like a fabric weave. They are most effective and useful for low frequencies and provide flexibility, mechanical strength, and life to the cable.
They are not very powerful, but they can reduce or put an end to EMIs/RMIs in your workplace or factory. Braided shielding dates back to the rise of the shoelace industry. Back then, many entrepreneurs experimented with their machines. Machines that made shoelaces were later programmed for making braids. For one, more mechanical support to the cable, with a coverage range as high as 95%. Plus, the choice of foil-supplemented braid cables helped too.
These cables today offer maximum shield coverage. It’s why you can find them at all mill operating applications. Since they are difficult to terminate, they last longer as well. In brief, here are some of the things to note about braided shielding:
- Greater flexibility and longevity of the cable.
- Enhanced mechanical power and strength.
- Ensures long-lasting physical protection.
- You can use a combination with foil for optimum results.
- Costly to produce.
- Typically, slow and difficult to terminate
- Offers around 45%-98% coverage.
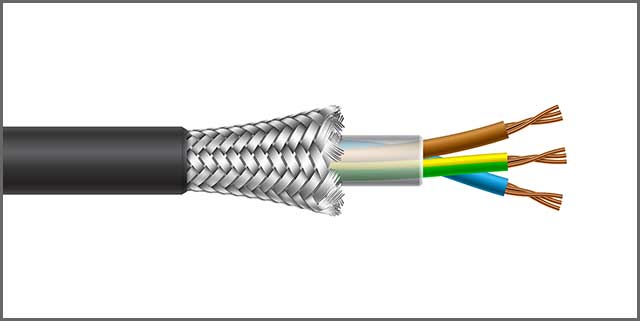
Metal-coated Mylar or Foil Shielding
Foil Shields or metal-coated Mylar comprised of Mylar composite tape and aluminum. Therefore, these shields are very light weighted and efficient. They are also very inexpensive and very easy to produce than normal braided shields. These generally look like the foil wrapped around in gum wrapper. Their application methods are also typically easy than other types of shields. They are more profitable for business startups or regular factories or offices.
They can reach up to 100% coverage. Also, diminish all kinds of electrical interferences or radiofrequency disturbances. They are easier to terminate than a braided shield, and all you require is a drain wire which goes into the ground.
Some of the key factors of foil shielding are:
- Easy to apply.
- Easy to produce.
- Lightweight and thin.
- Cheaper than braided shielding.
- Combination possibility with braided shields to generate maximum output and increase the coverage area.
- Less physical protection.
- Zero mechanical strength.
- Drain wire required
Spiral Shielding
Spiral Shielding is very similar to Braided Shielding. The main difference is the wrapping around a conductor or cable’s core, including the spirally wound single strand. There are several advantages to this shield. Some of them are:
- Much more flexible than your typical braided cable.
- Has a much wider coverage range than a braided shield which varies from 90%-99%.
- Easier to terminate than braided shields.
- Gives you more control over the EMIs/RMIs.
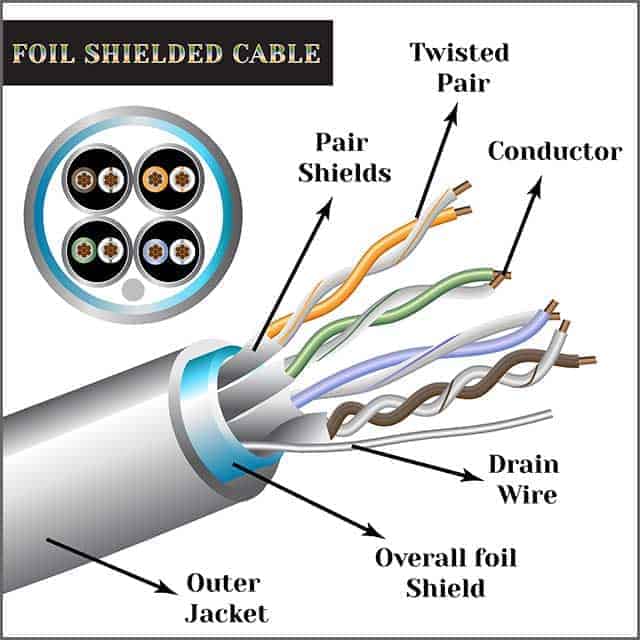
Chapter 4: The Application of Shielded cable
So, which devices normally use a shielded cable?
• Shielded Audio Cable
Shielded Audio Cables are capable of defending any interference. It prevents unwanted noise from mixing in with the original audio signal. Audio cables transport audio signals from one end to another, and this is their main functionality. A shielded audio cable delivers more accurate signals within the cable, giving you the best possible results.
• Shielded Power Cable
High voltage and medium voltage power cables are generally coated with a shield. This shielded layer consists of aluminum, copper, or conducting polymer. An unshielded, insulated wire cable that is in close contact with the earth can create a vast field of electrostatics. It also results in corona discharge. This discharge destroys the insulation.
Exposure to raw high-power voltages often results in accidents and electrical shocks. A shielded cable will prevent the occurrence of the vast electrostatic field. It ensures safety when dealing with power cables or machines that run through them.
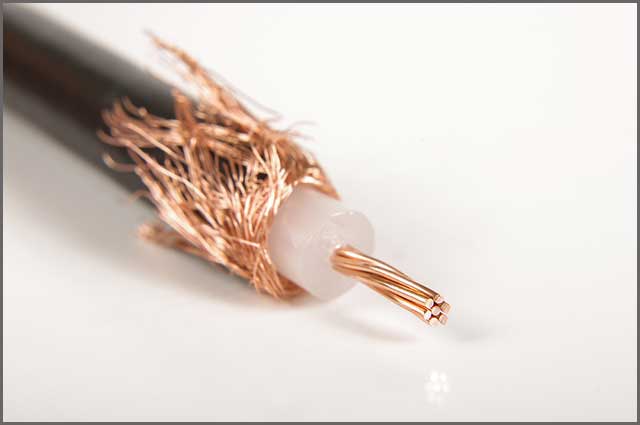
• Shielded Coaxial Cable
A coaxial cable functions as a transmitter of radio frequencies from one point to another. It is also known as coax cable. Coax cables are very useful and effective. Their shielded designs allow them to transmit data or radio frequencies from one point to another at a much faster rate. It works through a central conductor, generally a copper wire that carries audio and video signals. A dielectric plastic insulator wraps and encloses the copper wire. A braided mesh extracted from copper then shields the cable from EMIs/RMIs.

• Shielded USB Cable
A shielded USB cable is simply a USB cable that features a fast transfer of data. It is important to maintain and observe a balance of five conductors when it comes to making USB cables. These include two power supply wires, one wire for shielding, and a differential pair for communication. A shielded USB helps in the protection of data and efficient use of time by performing fast and quick actions.
Chapter 5: Things to Note about Shielded cables

It is important to keep in mind that the connector is one of the most important parts of the cable. Here are a few things that you need to know that will help you get the best results.
1. Ensure you have a proper ground connection with the connector
Doing this ensures the safety of the workers. You should check between the ground point and the equipment.
This way, you don’t have to worry about any accidents in the workplace, which could lead to other problems. Do know that high-power consuming machines can break down if not wired properly. Grounding the cables at one end also ensures that you don’t have to worry about noise producing ground loops.
2. Don’t Forget the Importance of the Connector
You can use braided shielding to get as much as 70-95% protection from EMI. While foil shielding offers 100% protection, they can be more difficult to work with, especially when using a connector. When selecting a connector, you need to ensure that the connector design offers a shielding capability that goes in sync with the cable.
3. Use the right Cable
If you don’t have a cable for sufficient shielding for the application needs, it could be a problem. If there is a noisier environment, we suggest going in for the braid combinations.
Chapter 6: Custom Shielded Cable Service
When installing shielded cables, it is up to you to study the environment and decide upon your desired shielding.
However, first, you have to study your environment accurately. It is because different environments require different types of shielding. Customise your shielded cables by alternating conductors and shield materials. You may get the ultimate shielded cable which matches and fits your exact requirements.
With our custom shielded cable service, you don’t have to worry about anything. We understand how important it is to choose the right shield type. We know you need the right material. Or, the ideal amount of coverage. It’s what, after all, what will help you get more productivity of cable systems.
We will help you create custom shielded cables that meet your needs, creating the appropriate shields for you that minimize most interference and ensures better and productive signal communication with the different cable systems.
We will ensure that:
- You don’t have to worry about poor connectors
- All cables minimize interference
- Use the right shielded cable type for you
- Guide you on what’s right for your needs
Come, talk to us about your shielded cable requirements. We will love to help!

Conclusion
Shielded cables are thus very useful and guarantee safety. Working with huge powerful electrical motors and machines become easy with shielded cables. It is a must for every business to adapt and customise their required shielding. Ensure a more sustainable and safe working environment for the whole company.
By installing these cables, you ensure you get the most out of your investments by reducing data loss, signal loss, and power loss. Contact us today for your customised shielding cable needs, and let us help you get tailored solutions.
Hommer Zhao
Hommer Zhao serves as Director of Wiringo, leveraging a wealth of expertise in custom wire harness and cable assembly.
Drawing on more than a decade of hands-on expertise in the electronics field, Hommer focuses on wire harness manufacturing, custom cable assembly, and expedited restricted product production. His operations include a pair of wire harness production facilities and two dedicated PCB manufacturing & PCBA sites, all strategically located across Shijiazhuang, Shenzhen, Jiangmen, and the Philippines.
Hommer frequently refers to resources like Wiring Harness News for up-to-date insights and methods related to wire harness production.
Beyond his research and reading, Hommer also contributes to the Wiring Harness Manufacturer’s Association (WHMA), which offers invaluable resources and professional guidelines to wire harness specialists.
Get Your Free Sample!
Explore our custom services now. Email us at [email protected] for more details.



